Floor Systems
Floor systems include mezzanines, catwalks and walkways with all their components and subsystems such as joists, grating, checkered plates, staircases and handrails.
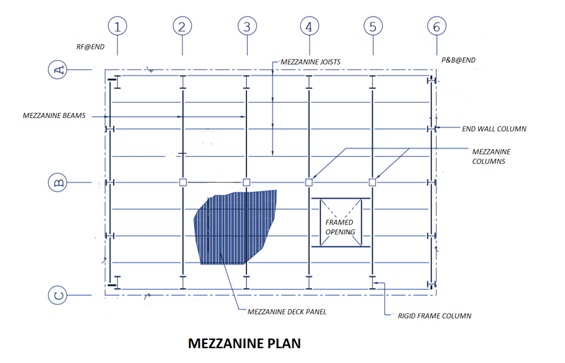
Mezzanine
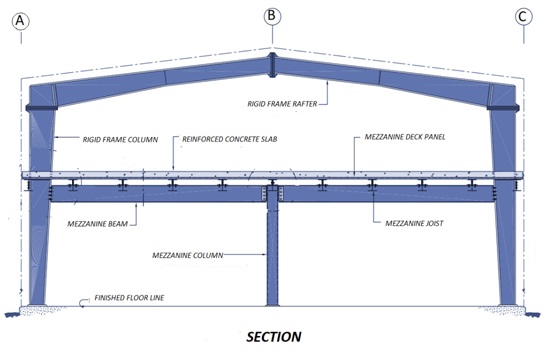
A mezzanine is an elevated flooring system located inside the outer shell of a pre-engineered steel building. The most common uses of a mezzanine are to accommodate offices or to serve as a storage area. Generally, the mezzanine framing is connected to the main rigid frame columns for lateral stability. Primary and secondary mezzanine members are analyzed as pinned at both ends. Though this design approach may result in a slightly heavier design, it has proven to be safer in the long term due to the possibility that the mezzanine may be partially removed as building layouts change during the lifetime of a structure.
Mezzanine structures consists of built-up or hot rolled main mezzanine beams that support built-up, hot rolled or cold-formed mezzanine joists which, in turn, support a metal deck. A reinforced concrete slab is cast on the metal deck as the finished surface. The metal deck is not designed to carry the floor live loads; it is intended only to carry the reinforced concrete slab during pouring. The reinforced concrete slab must be designed to carry the floor loads.
Roof Platform
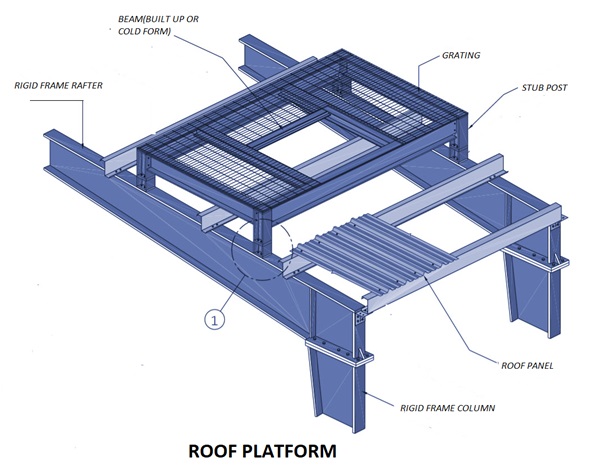
A roof platform is a structural framing system mounted on top of the roof and is specifically designed to support heavy roof accessories, such as HVAC units, water tanks and other miscellaneous roof equipment.
Roof platforms are made of hot rolled, built-up or cold-formed sections supported by built-up or tube stub post sections, which are bolted to the top of the rafter flanges. Bracing is sometimes provided in both directions to ensure the stability of the framing system.
Roof platforms are designed in such a way so as to permit the removal of the roof sheeting, if so desired, with minimum effort. When a platform is required to support equipment it is recommended that it be large enough to provide access around the equipment for future maintenance of the equipment
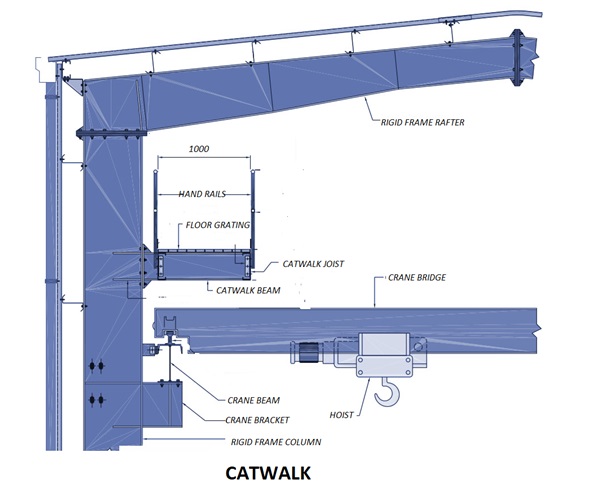
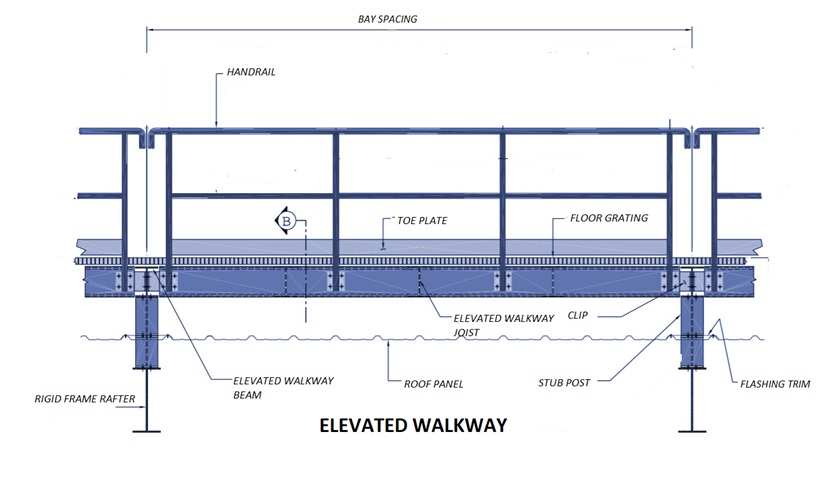
Catwalks and Walkways
Catwalks and Walkways which are used primarily by maintenance crews to provide access to mechanical equipment:
• Catwalks that are normally located inside the building alongside crane beams or suspended underneath rigid frame rafters.
• Elevated walkways that are placed directly above the building roof, whenever very frequent access is required between several roof platforms.
In most buildings, access to the roof is limited to a few external or internal locations. When the access to a roof is external, walkways are laid between the initial access point to the roof and the equipment-supporting platforms on the roof.
It is highly recommended to consider the provision of walkways early in the design stage of pre-engineered steel buildings. Roof sheeting is not intended to support very frequent access and may be damaged if service men are not aware of its limitations. When heavy equipment is supported on roof platforms, access to those platforms should be properly laid out to avoid causing damage to the roof sheets, which in turn may result in roof leaks.
When walking on roof sheeting, care must be taken not to step on the high rib portion of the roof sheeting profile.
Catwalks and elevated walkways are generally provided with handrails for safety. Decking for catwalks and walkways can be either galvanized grating or checkered plates.
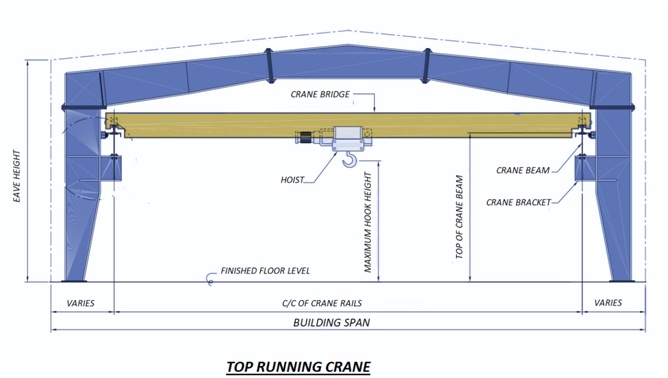
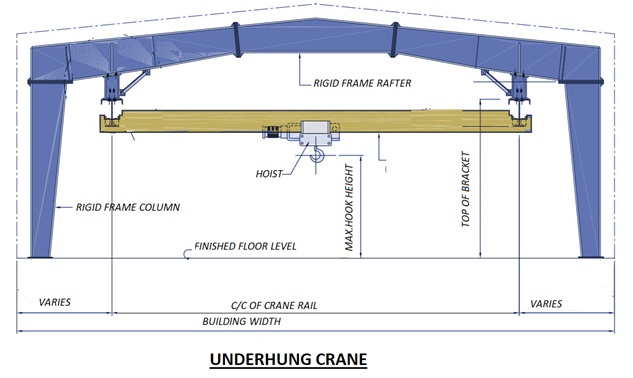
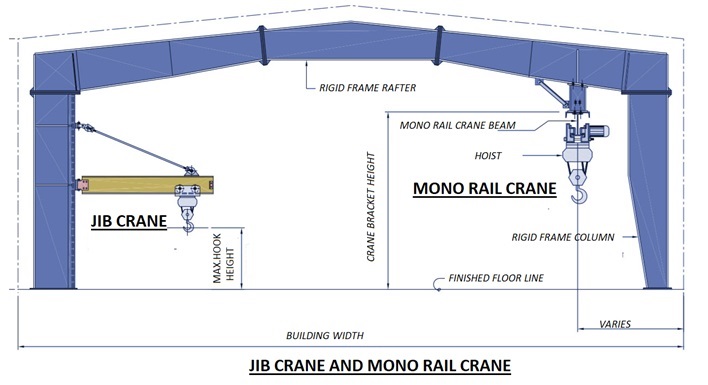
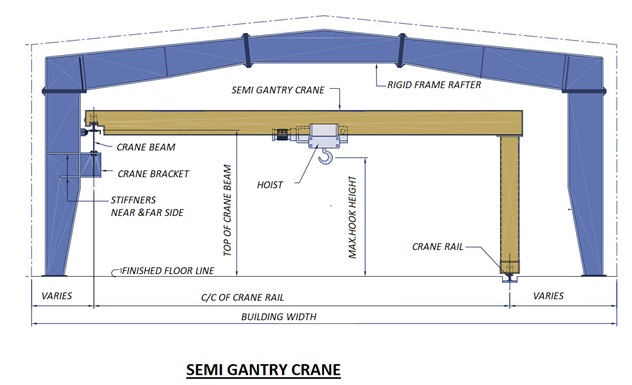
Crane Systems
All pre-engineered steel buildings can be designed for crane operation provision as per operational need. There is various type of crane being used in industry for various purposes. For each type of crane, there is a suitable design criteria for PEB design and structure can be adequately designed to meet the functional requirements.
The most common types of crane systems in pre- engineered steel buildings are: